
- The law of one price: similar things must have similar prices
- Replication: the only reliable way to value a security
- A simple up-down model for the risk of stocks, in which expected return
- The Law of one price leads to CAPM for stocks
- Replicating derivatives via the law of one price
Replication
replication의 아이디어는 이미 가격을 알고 있는 비슷한 financial instruments로 가격을 모르는 상품의 가격을 알고자 하는 것
The one law of quantitative finance
If 2 securities have identical payoffs under all possible future scenarios, then the 2 securities should have identical current prices
It should be impossible to obtain for zero cost a security that has non-negative payoffs in all future scenarios, with at least 1 scenario having a positive payoff
In the long run, in liquid markets, the law of one price usually holds. In practice, in the short run, in illiquid markets or during financial crises and panics, the law of one price may not hold.
Valuation by replication
To estimate the unknown value of a target security, find some replicating portfolio, a set of more liquid securities with known prices, that has the same payoffs as the target, no matter how the future turns out.
To demonstrate the target and the replicating portfolio have identical future payoffs under all circumstances.
- specify what you mean by ‘under all circumstances’ for each security
- find a strategy for creating a replicating portfolio that, in each future scenario or circumstance
We must create a replicating portfolio of liquid securities whose payoffs match the payoffs of the target in all future scenarios.
Styles of replication
Static replication
- When finish construction of replicating portfolio, no need additional trading required for the lifetime of the target security
Dynamic replication
- The components and weights of replicating portfolio must change over time
- Need to continually trade as time passes and the prices of the underlying securities in order to maintain the replication
1973년 Black-Scholes equation은 option의 dynamic replication을 가능하게 해준 일대의 사건
The limits of replication
All financial models are based on assumptions
At best, therefore, financial models are only approximations to reality. Understanding the assumptions of financial models is the key to understanding the limits of replication.
replication steps
- Capture the reality as much as possible
- Determining weights matters at all, in theory in replication
- In reality, adjusting weights by trading is problematic - bid-ask spread, market impact, financing costs, transaction costs, operational risks, impossible-to-observed variables (ex. future volatility)
In actual markets, replicating strategy is rarely found. Economic model can be the alternatives. However, it is a matter of how people feel. So that, utility functions underlying the economic model are the hidden variables of economic theory, quantities never directly observed.
Modeling the risk of underliers
modeling은 underliers의 behavior를 나타내는 것으로 시작
modern portfolio theory는 efficient market hypothesis에 기반을 두고 있는데, 이는 2007-2008년 금융위기를 기점으로 비판을 받고 있음
The efficient market hypothesis
1960년대 University of Chicago를 위시로 한 Eugene Fama는 Efficient market hypothesis를 발표
이는 이후 몇년간 수학적인 발전을 이뤄 종국에는 strong, weak 등과 같은 efficiency의 정도를 구분하는 것으로 정리되었다.
EMH는 장기적으로 시장을 이기는 것은 불가능하고, 이는 현재의 모든 경제와 시장의 정보가 가격에 반영되어있기 때문이라고 주장했다. 이는 systmetic하게 가격을 예측하는 것이 불가능하니 이를 가설로 만들어 버린 것으로도 볼 수 있다.
Uncertainty, risk, and return
Risk is quantifiable but uncertainty is not quantifiable.
The risk of stocks
The most important feature of a stock is the uncertainty of its returns.
The volatility is a measure of the stock’s risk.
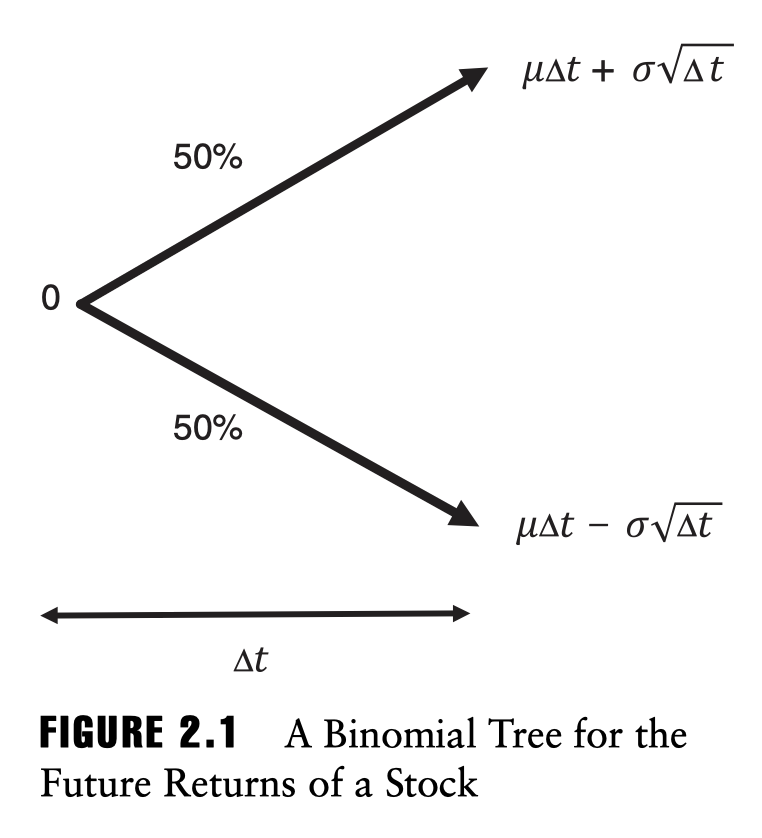
Binomial model의 특징은 expected return과 volatility로 주가의 움직임을 타나낸다는 점인데, 이는 굉장히 강한 가정임에 틀림없다. 그러나 the law of one price와 결부되어 CAPM, Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing formula까지 발전한다.
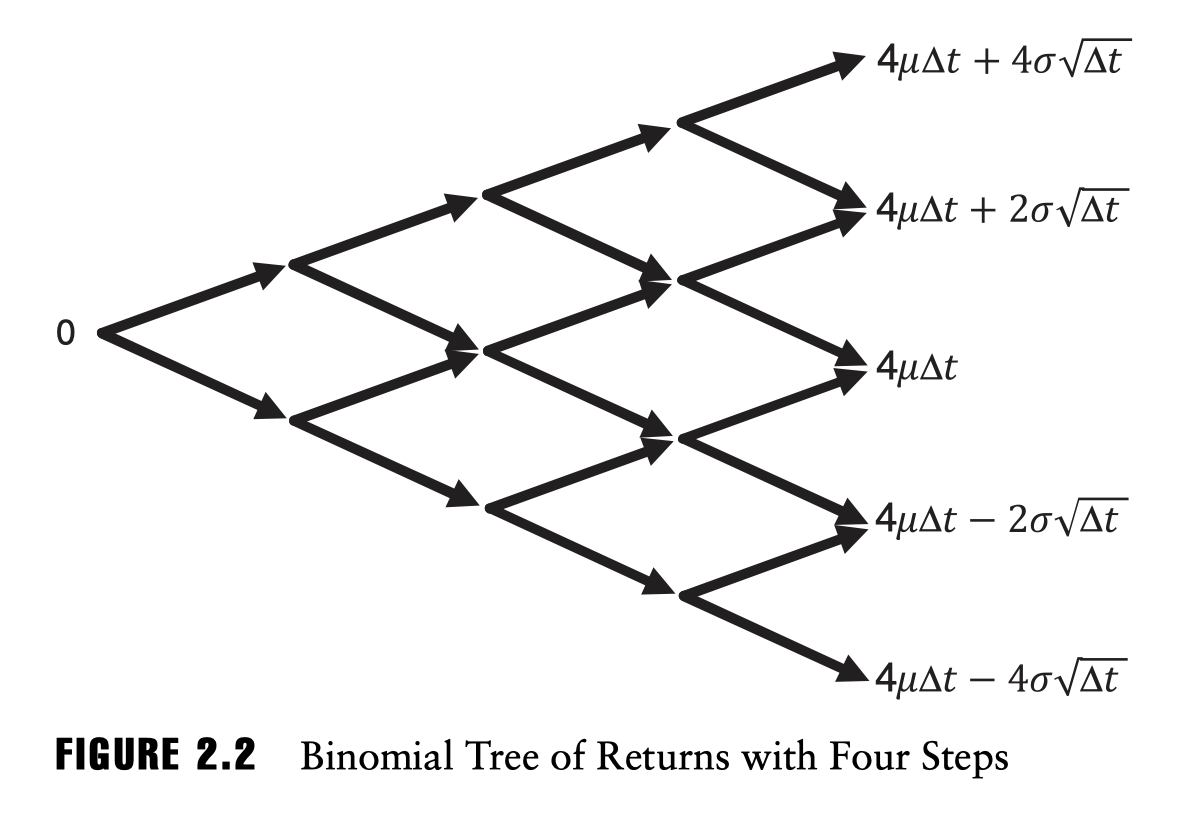
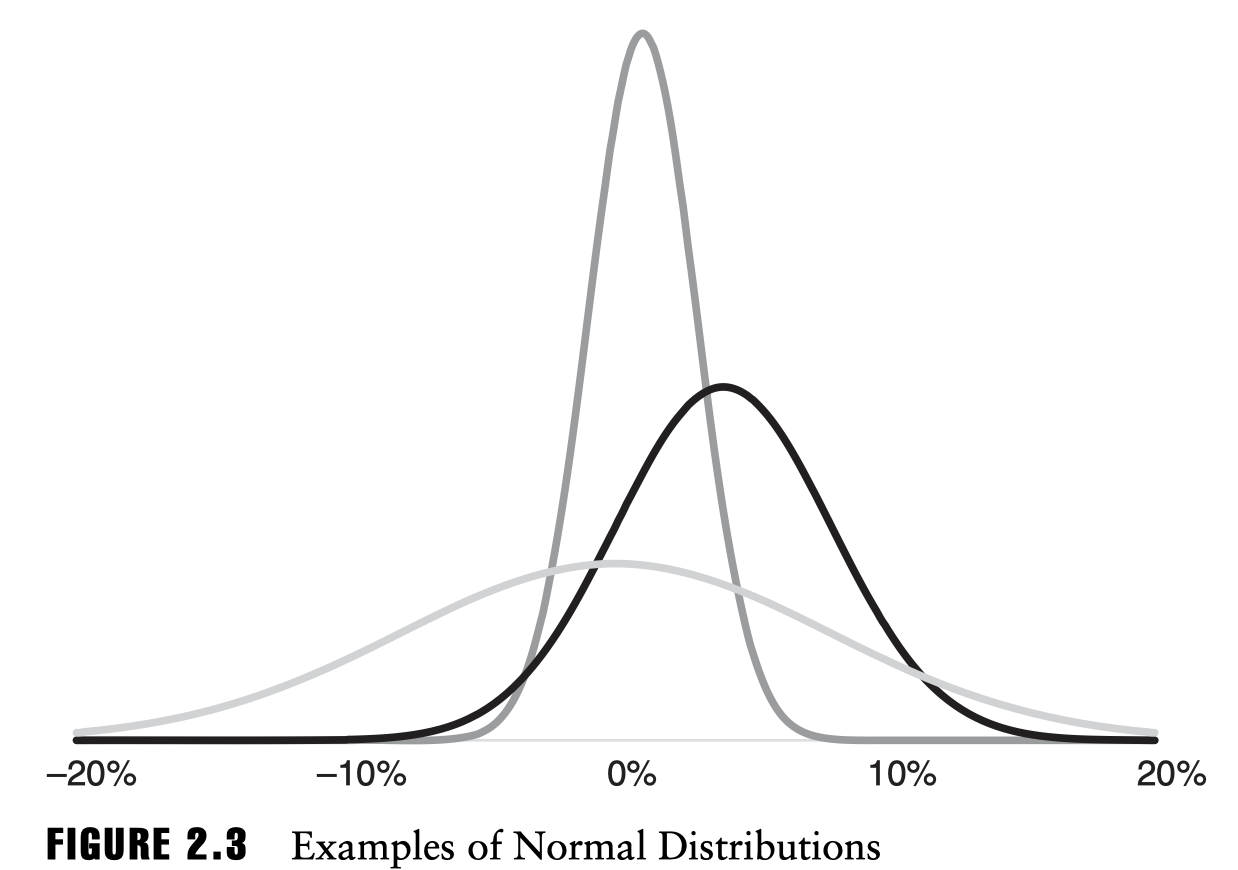
아주 간단한 모델에서는 symmetric distribution을 사용하는데 이는 일반적으로 negative skewness를 가지는 주가 수익률의 분포와는 다소 거리가 있다. ex) fat tail
그러나 symmetric distribution은 modeling을 배우기에 아주 좋은 시작점이다. 실제 주가의 움직임은 굉장히 복잡하고 예측불가능하지만, binomial model은 직관적으로 쉬운 접근법을 제시한다.
Riskless bonds

The riskless rate is ubiquitous throughout economics and finance and is central to the replication and valuation of options.
riskless bond의 binomial tree를 그리면 가격은 up과 down 사이에 넣이게 될텐데, 그 어떤 경우에라도 riskless이기 때문에 positive payoff를 나타내는 모순이 발생한다. - 솔직히 이거 왜 설명하는지 모르겠지만
In the reality, the US treasury bill is commonly considered as a riskless rate.
Key question of investing
What anticipated possible future reward justifies a particular anticipated risk?
The law of one price states that securities with identical payoffs under all possible circumstances should have identical prices.
With in the binomial framework
- What is the relation between expected return and volatility?
Some investment risks can be avoided
The law of one price says that the securities with identical risk should have identical expected returns
There are 2 types of risk
- avoidable risk - by diversification, dilution, or hedging
- unavoidable risk
So that, the law of one price is restated as
Identical unavoidable risks should have identical expected returns
Assumptions
- It has the same return as other unavoidable risks of the same size
- The principle of replication applies to it and all other securities
The results we deduce in those worlds will logically consistent, but will not resemble the relation between expected return and volatility in actual market.
Derivatives are not independent securities

A derivative is a contract
abhor


